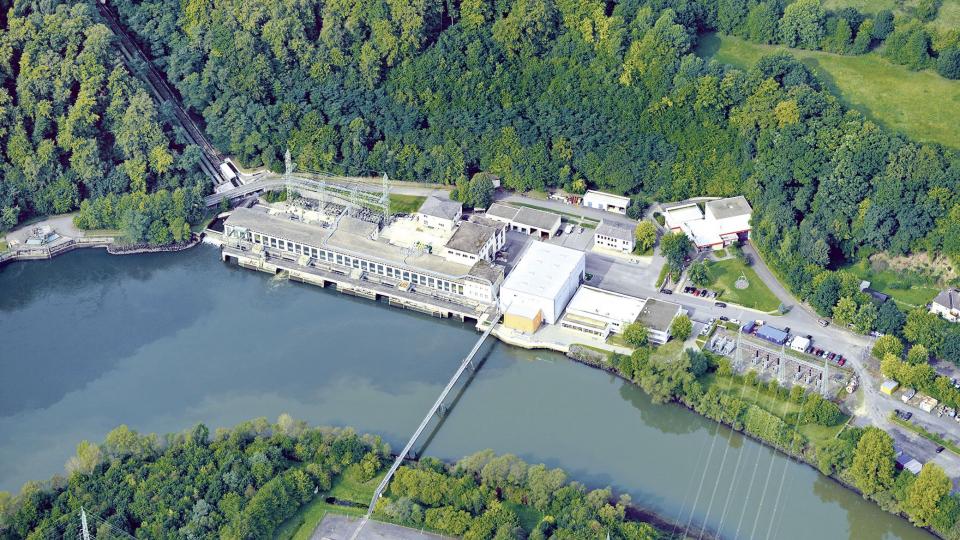
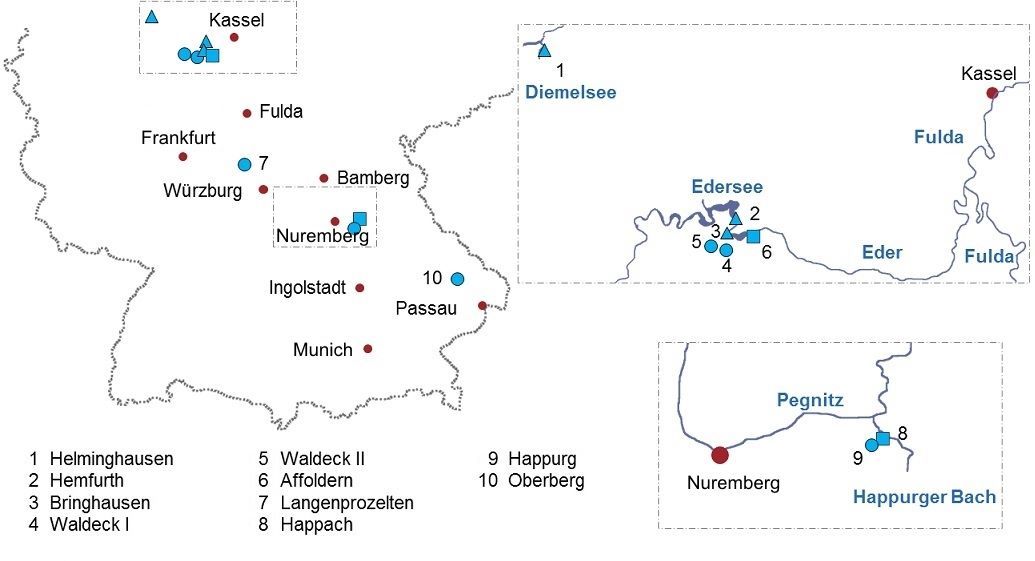
The Pumped storage power plant group (PSW) operates five pumped storage power plants with a capacity of 884 megawatts. With an annual generating capacity of around 1.3 billion kilowatt hours, the PSWs make an important contribution to the security of supply. The power plant group also includes three storage power plants and one run-of-river power plant, both owned and operated, with a total capacity of 93 megawatts, which generate 54 gigawatt hours of climate-friendly electricity per year and save over 31,000 tons of CO2.
Overview of the power plants within the Pumped storage hydropower group
Our PSWs store surplus electricity in the form of positional energy by pumping water from a reservoir to higher ground. When needed, the water is released from the upper reservoir to drive turbines located lower down, thereby converting the potential energy of the water back into electricity. With an overall efficiency of up to 80 percent, pumped storage technology is currently not only the only way to store large amounts of energy effectively and permanently, but also the most environmentally friendly.
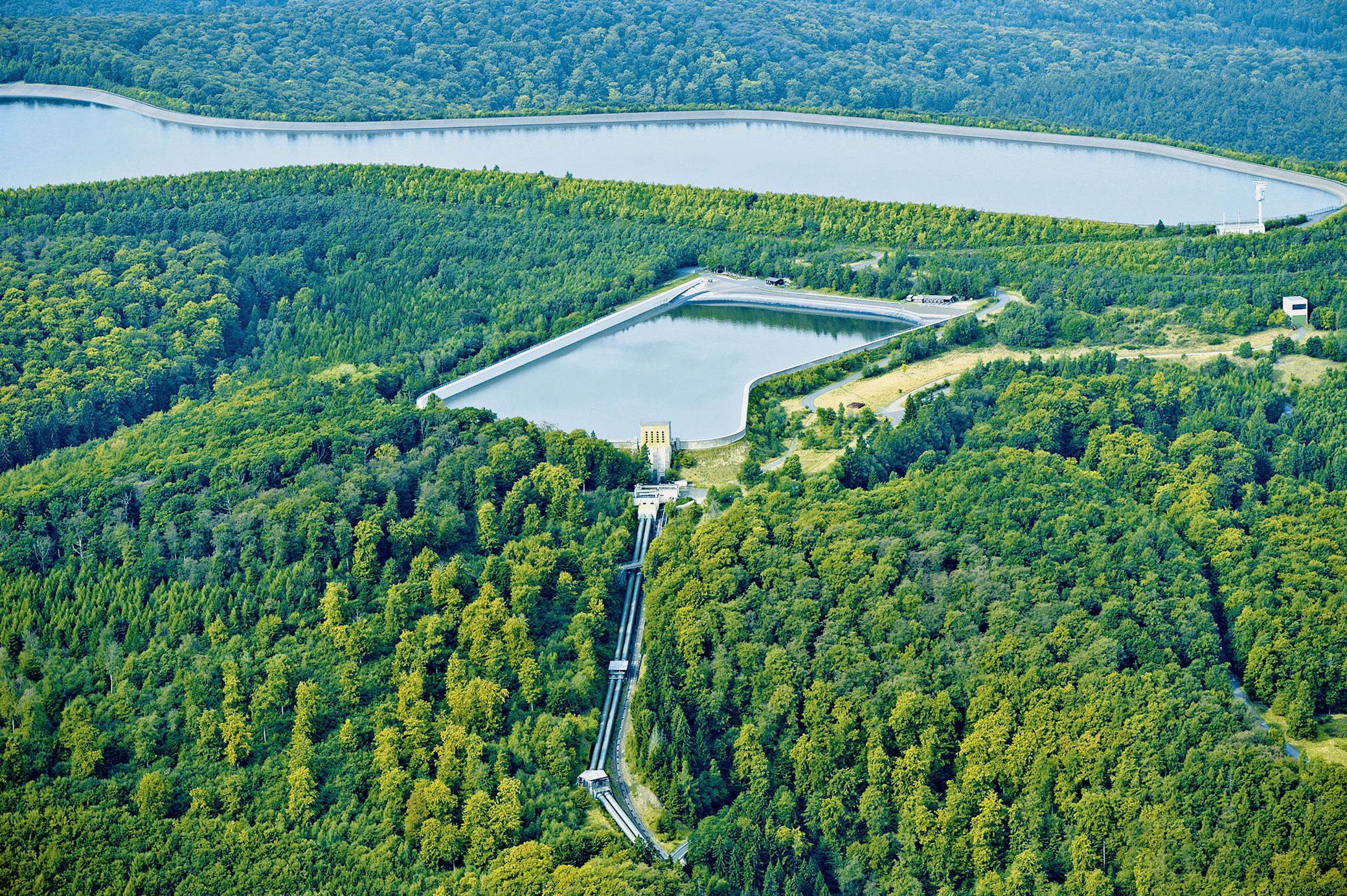

Waldeck Oberbecken
In addition to storing surplus electrical energy, PSWs are of crucial importance for grid stability due to their rapid availability and controllability. They are an important prerequisite for the integration of renewable power generation from wind and photovoltaic plants, which cannot be regulated. In addition to balancing grid fluctuations, frequency and voltage regulation, the PSW are also available for grid reconstruction or black start after a "blackout".
The Langenprozelten pumped storage power plant is the only pumped storage power plant in Deutsche Bahn's power grid and thus plays an important role in grid stability and power supply for traction current.

| Location | Eder, Diemel, Main, Sinn, Happach, and Rusel, Germany |
| Total installed capacity | 807 MW |
| Average annual generation | 1,300 GWh |












